Aug 2025
Computer Vision and Reinforcement Learning Pipeline
Top: three objects featurized based on colour.
Bottom: three objects featurized based on shape.
As part of my work at the BLINC Lab during the summer of 2025 and continuing into the fall, I developed a computer vision and reinforcement learning (RL) pipeline intended to be used with the HANDi Hand.
I developed this system in the context of grasp prediction and adaptive switching for robotic hands. The fundamental objective behind this project is to predict the grasp that a hand would need to perform, based on visual information collected by a camera.
I presented part of this work with a poster at the Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry (FoMD)’s 58th Annual Summer Students’ Research Day.
Here is an overview of the pipeline:
A camera provides a video stream.
Computer vision techniques are used to process the video stream so that edges are white and everything else is black.
Again, computer vision techniques are used to identify the most prominent shape (contour) in the video stream of black and white edges.
Once more, computer vision techniques are used to mask the original video feed around the identified shape (circle, rectangle, or triangle) and then determine its primary colour (red, green, or blue).
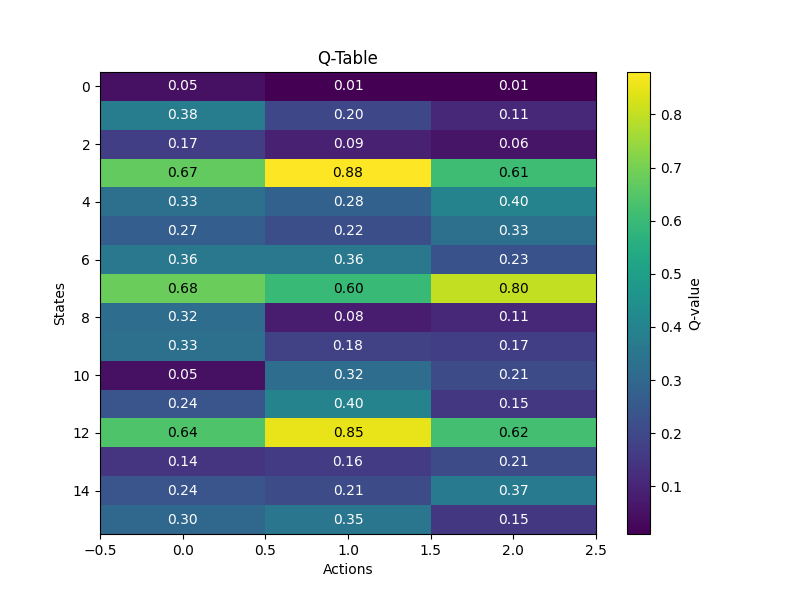
The colour and shape information is tile-coded and provided to a reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm known as TD-Lambda.
The RL algorithm learns from experience over multiple episodes to predict which grasp (action) is appropriate based on information (state) about the objects presented in the video stream.
Top: screenshot of how the camera views the world by edge detection. Bottom left: reward vs. training steps plot showing that the RL agent is capable of learning. Bottom right: Q-table visualizing how the RL agent decides which action to take.